
Gewichte und Maße
| Länge | von 18 bis 22 cm |
|---|
Biologische Daten
| Lebensdauer | von 20 bis 40 Jahre |
|---|
Gefährdungsstatus
| Gefährdet |
Beschreibung des Tieres
DerivativeAndIntegralProblem.java in the folder lectures/week1_2 of the course site.import java.util.Scanner;
public class DerivativeAndIntegralProblem {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scanner.nextInt();
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
int[] coefficients = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
coefficients[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int derivativeValue = calculateDerivativeValueAt(coefficients, n, a);
int integralValue = calculateIntegralValueBetween(coefficients, n, a, b);
System.out.println(derivativeValue);
System.out.println(integralValue);
}
public static int calculateDerivativeValueAt(int[] coefficients, int n, int x) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
result += coefficients[i] * i * Math.pow(x, i - 1);
}
return result;
}
public static int calculateIntegralValueBetween(int[] coefficients, int n, int a, int b) {
int resultA = 0;
int resultB = 0;
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
resultA += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(a, i + 1) / (i + 1);
resultB += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(b, i + 1) / (i + 1);
}
return resultB - resultA;
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Read the number of coefficients
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// Read the coefficients into an array
int[] coefficients = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
coefficients[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// Read the point to evaluate the derivative and the bounds for integration
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
// Calculate and print the derivative at point x
int derivativeAtX = calculateDerivativeAtX(coefficients, x);
System.out.println(derivativeAtX);
// Calculate and print the integral from a to b
int integralFromAToB = calculateIntegralFromAToB(coefficients, a, b);
System.out.println(integralFromAToB);
}
// Method to calculate the derivative of a polynomial at a given point x
private static int calculateDerivativeAtX(int[] coefficients, int x) {
int derivative = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
derivative += i * coefficients[i] * Math.pow(x, i - 1);
}
return derivative;
}
// Method to calculate the integral of a polynomial from a to b
private static int calculateIntegralFromAToB(int[] coefficients, int a, int b) {
double integralA = 0;
double integralB = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
integralA += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(a, i + 1) / (i + 1);
integralB += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(b, i + 1) / (i + 1);
}
return (int) (integralB - integralA);
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Read the number of coefficients
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// Read the coefficients into an array
int[] coefficients = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
coefficients[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// Read the point to evaluate the derivative and the bounds for integration
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
// Calculate and print the derivative at point x
int derivativeAtX = calculateDerivativeAtX(coefficients, x);
System.out.println(derivativeAtX);
// Calculate and print the integral from a to b
int integralFromAToB = calculateIntegralFromAToB(coefficients, a, b);
System.out.println(integralFromAToB);
}
// Method to calculate the derivative of a polynomial at a given point x
private static int calculateDerivativeAtX(int[] coefficients, int x) {
int derivative = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
derivative += i * coefficients[i] * Math.pow(x, i - 1);
}
return derivative;
}
// Method to calculate the integral of a polynomial from a to b
private static int calculateIntegralFromAToB(int[] coefficients, int a, int b) {
double integralA = 0;
double integralB = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
integralA += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(a, i + 1) / (i + 1);
integralB += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(b, i + 1) / (i + 1);
}
return (int) (integralB - integralA);
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Read the number of coefficients
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// Read the coefficients into an array
int[] coefficients = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
coefficients[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// Read the point to evaluate the derivative and the bounds for integration
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
// Calculate and print the derivative at point x
int derivativeAtX = calculateDerivativeAtX(coefficients, x);
System.out.println(derivativeAtX);
// Calculate and print the integral from a to b
int integralFromAToB = calculateIntegralFromAToB(coefficients, a, b);
System.out.println(integralFromAToB);
}
// Method to calculate the derivative of a polynomial at a given point x
private static int calculateDerivativeAtX(int[] coefficients, int x) {
int derivative = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
derivative += i * coefficients[i] * Math.pow(x, i - 1);
}
return derivative;
}
// Method to calculate the integral of a polynomial from a to b
private static int calculateIntegralFromAToB(int[] coefficients, int a, int b) {
double integralA = 0;
double integralB = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
integralA += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(a, i + 1) / (i + 1);
integralB += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(b, i + 1) / (i + 1);
}
return (int) (integralB - integralA);
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Read the number of coefficients
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// Read the coefficients into an array
int[] coefficients = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
coefficients[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// Read the point to evaluate the derivative and the bounds for integration
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
// Calculate and print the derivative at point x
int derivativeAtX = calculateDerivativeAtX(coefficients, x);
System.out.println(derivativeAtX);
// Calculate and print the integral from a to b
int integralFromAToB = calculateIntegralFromAToB(coefficients, a, b);
System.out.println(integralFromAToB);
}
// Method to calculate the derivative of a polynomial at a given point x
private static int calculateDerivativeAtX(int[] coefficients, int x) {
int derivative = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
derivative += i * coefficients[i] * Math.pow(x, i - 1);
}
return derivative;
}
// Method to calculate the integral of a polynomial from a to b
private static int calculateIntegralFromAToB(int[] coefficients, int a, int b) {
double integralA = 0;
double integralB = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
integralA += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(a, i + 1) / (i + 1);
integralB += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(b, i + 1) / (i + 1);
}
return (int) (integralB - integralA);
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Read the number of coefficients
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// Read the coefficients into an array
int[] coefficients = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
coefficients[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// Read the point to evaluate the derivative and the bounds for integration
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
// Calculate and print the derivative at point x
int derivativeAtX = calculateDerivativeAtX(coefficients, x);
System.out.println(derivativeAtX);
// Calculate and print the integral from a to b
int integralFromAToB = calculateIntegralFromAToB(coefficients, a, b);
System.out.println(integralFromAToB);
}
// Method to calculate the derivative of a polynomial at a given point x
private static int calculateDerivativeAtX(int[] coefficients, int x) {
int derivative = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
derivative += i * coefficients[i] * Math.pow(x, i - 1);
}
return derivative;
}
// Method to calculate the integral of a polynomial from a to b
private static int calculateIntegralFromAToB(int[] coefficients, int a, int b) {
double integralA = 0;
double integralB = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
integralA += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(a, i + 1) / (i + 1);
integralB += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(b, i + 1) / (i + 1);
}
return (int) (integralB - integralA);
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Read the number of coefficients
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// Read the coefficients into an array
int[] coefficients = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
coefficients[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// Read the point to evaluate the derivative and the bounds for integration
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
// Calculate and print the derivative at point x
int derivativeAtX = calculateDerivativeAtX(coefficients, x);
System.out.println(derivativeAtX);
// Calculate and print the integral from a to b
int integralFromAToB = calculateIntegralFromAToB(coefficients, a, b);
System.out.println(integralFromAToB);
}
// Method to calculate the derivative of a polynomial at a given point x
private static int calculateDerivativeAtX(int[] coefficients, int x) {
int derivative = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
derivative += i * coefficients[i] * Math.pow(x, i - 1);
}
return derivative;
}
// Method to calculate the integral of a polynomial from a to b
private static int calculateIntegralFromAToB(int[] coefficients, int a, int b) {
double integralA = 0;
double integralB = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
integralA += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(a, i + 1) / (i + 1);
integralB += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(b, i + 1) / (i + 1);
}
return (int) (integralB - integralA);
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Read the number of coefficients
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// Read the coefficients into an array
int[] coefficients = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
coefficients[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// Read the point to evaluate the derivative and the bounds for integration
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
// Calculate and print the derivative at point x
int derivativeAtX = calculateDerivativeAtX(coefficients, x);
System.out.println(derivativeAtX);
// Calculate and print the integral from a to b
int integralFromAToB = calculateIntegralFromAToB(coefficients, a, b);
System.out.println(integralFromAToB);
}
// Method to calculate the derivative of a polynomial at a given point x
private static int calculateDerivativeAtX(int[] coefficients, int x) {
int derivative = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
derivative += i * coefficients[i] * Math.pow(x, i - 1);
}
return derivative;
}
// Method to calculate the integral of a polynomial from a to b
private static int calculateIntegralFromAToB(int[] coefficients, int a, int b) {
double integralA = 0;
double integralB = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
integralA += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(a, i + 1) / (i + 1);
integralB += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(b, i + 1) / (i + 1);
}
return (int) (integralB - integralA);
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Read the number of coefficients
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// Read the coefficients into an array
int[] coefficients = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
coefficients[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// Read the point to evaluate the derivative and the bounds for integration
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
// Calculate and print the derivative at point x
int derivativeAtX = calculateDerivativeAtX(coefficients, x);
System.out.println(derivativeAtX);
// Calculate and print the integral from a to b
int integralFromAToB = calculateIntegralFromAToB(coefficients, a, b);
System.out.println(integralFromAToB);
}
// Method to calculate the derivative of a polynomial at a given point x
private static int calculateDerivativeAtX(int[] coefficients, int x) {
int derivative = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
derivative += i * coefficients[i] * Math.pow(x, i - 1);
}
return derivative;
}
// Method to calculate the integral of a polynomial from a to b
private static int calculateIntegralFromAToB(int[] coefficients, int a, int b) {
double integralA = 0;
double integralB = 0;
for (int i = coefficients.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
integralA += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(a, i + 1) / (i + 1);
integralB += coefficients[i] * Math.pow(b, i + 1) / (i + 1);
}
return (int) (integralB - integralA);
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// Read the number of coefficients
int n = scanner.nextInt();
// Read the coefficients into an array
int[] coefficients = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = n; i >= 0; i--) {
coefficients[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
// Read the point to evaluate the derivative and the bounds for integration
int x = scanner.nextInt();
int a = scanner.nextInt();
int b = scanner.nextInt();
// Calculate and print the derivative at point x
int derivativeAtX = calculateDerivativeAtX(coefficients, x);
System.out.println(derivativeAtX);
// Calculate and print the integral from a to b
int integralFrom
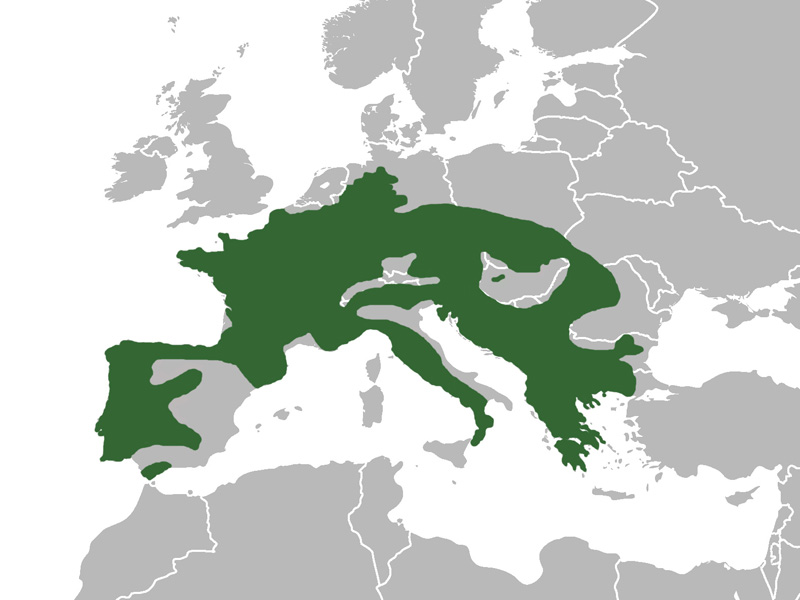
Verbreitungskarte
Ähnliche Tiere
Neue Tierfotos
Top 10 Tiere
- Nimmersatt (Mycteria ibis)
- Nase (Chondrostoma nasus)
- Erdspecht (Geocolaptes olivaceus)
- Amerikanische silbermöwe (Larus smithsonianus)
- Echte karettschildkröte (Eretmochelys imbricata)
- Seeigel (Echinoidea)
- Blaue pfau (Pavo cristatus)
- Veränderliche krabbenspinne (Misumena vatia)
- Schleie (Tinca tinca)
- Berggorilla (Gorilla beringei beringei)


